In the realm of cellular biology and biotechnology, the efficient disruption of cell membranes is a crucial step. Researchers and scientists leverage various methods to break down cell structures, releasing intracellular components for further analysis and extraction. Two widely employed techniques for cell disruption are sonication and homogenization, each presenting its unique set of advantages and considerations. In this comprehensive guide, we explore these methodologies to unravel the intricacies of cell disruption.
Samples for protein and nucleic acid analysis must be prepared in two steps: tissue disruption to liberate individual cells and lysis of those cells to release their cellular contents. Mechanical homogenization and sonication (also known as ultrasonic homogenization) are two common methods used in these procedures.
Choosing the best approach for your specific application requires significant consideration. Each has advantages and disadvantages, and laboratories frequently utilize these techniques in conjunction with one another. Continue reading to learn how to choose a procedure that will not harm valuable or irreplaceable tissue samples.
Sonication: Probing Cells, Enhancing Cell Disruption
Sonication involves the use of high-frequency sound waves to disrupt cell membranes. The process generates intense pressure waves that create microscopic bubbles in the cell suspension. As these bubbles collapse, they produce shock waves, leading to the mechanical disruption of cell structures.
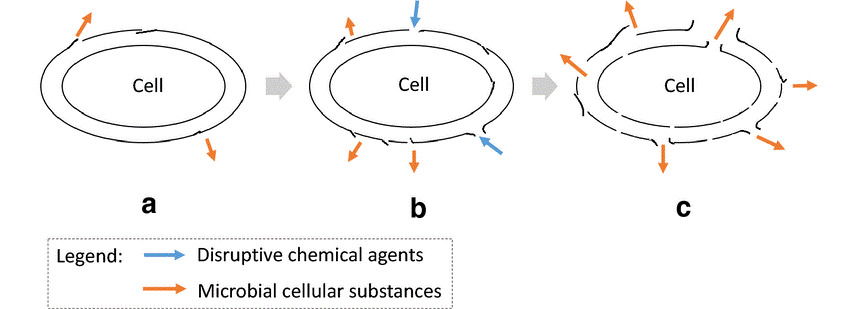
Benefits of Sonication:
- Precision and Control: Sonication offers precise control over the disruption process, allowing researchers to tailor the intensity and duration of sonication.
- Time Efficiency: Sonication is often a quick process, making it suitable for laboratories where time is of the essence.
- Scalability: It can be easily scaled for small to large volumes of cell suspension.
Considerations:
- Heat Generation: Intense sonication can lead to a rise in temperature, which might adversely affect sensitive biomolecules.
- Equipment Costs: High-quality sonication equipment can be relatively expensive.
Homogenization: The Mechanical Force Approach
Homogenization, on the other hand, relies on mechanical force to disrupt cells. In this process, cells are forced through a narrow space or punctured using mechanical blades, resulting in the breaking of cell walls.
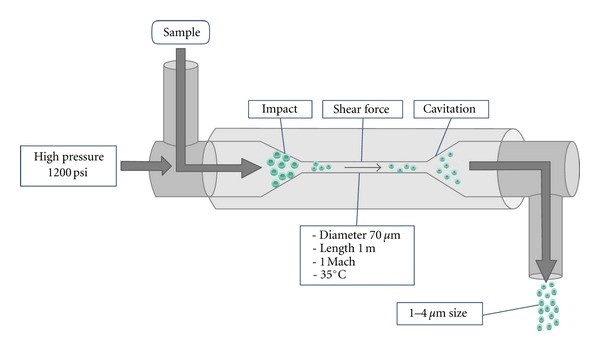
Benefits of Homogenization:
- Versatility: Homogenization can handle various sample types, from soft tissues to tough plant materials.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Homogenization equipment is generally more cost-effective compared to high-end sonication devices.
- Less Heat Generation: Homogenization tends to generate less heat, making it suitable for heat-sensitive samples.
Considerations:
- Less Precision: Achieving precise control over the disruption process might be challenging in homogenization, especially for smaller volumes.
- Sample Heating: While generally less than sonication, homogenization can still cause a moderate increase in sample temperature.
Choosing the Right Method
The choice between sonication and homogenization depends on various factors, including the sample type, required cell disruption level, and the downstream applications.
For DNA and RNA extraction, where preserving molecular integrity is crucial, sonication might be the preferred choice.
When dealing with larger volumes or more robust samples, homogenization could be the pragmatic approach.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of cellular research, the choice between sonication and homogenization is akin to selecting the right tool for a delicate task. Understanding the nuances of each technique empowers researchers to make informed decisions, ensuring optimal results in cell disruption.
As technology advances, researchers continue to refine and innovate these techniques, pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable in the realm of cell disruption. The journey from intact cells to liberated cellular components is a fascinating exploration that unfolds at the crossroads of biology and technology.
This blog aims to serve as a comprehensive guide, shedding light on the principles, benefits, and considerations associated with sonication and homogenization. With a thorough understanding of these techniques, researchers can navigate the complexities of cellular biology with precision and efficiency.